publications
2025
-
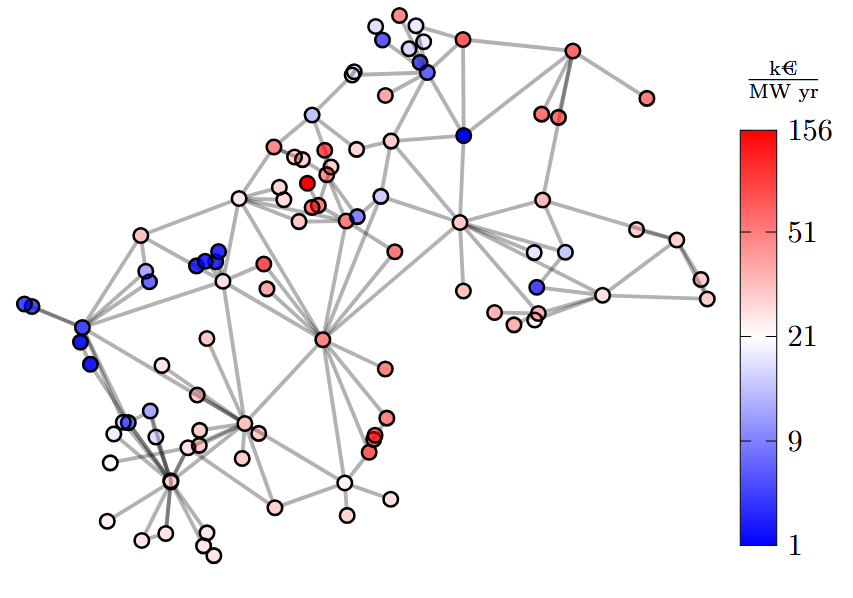 Power Generation Investment under Zonal Electricity Pricing with Market-Based Re-dispatchQuentin Lété, Yves Smeers, and Anthony PapavasiliouThe Energy Journal, 2025
Power Generation Investment under Zonal Electricity Pricing with Market-Based Re-dispatchQuentin Lété, Yves Smeers, and Anthony PapavasiliouThe Energy Journal, 2025There is currently an intense debate in Europe on the allocation of transmission capacity in the internal electricity market. In this context, the concept of market-based re-dispatch has regained considerable attention, as a candidate design to reconcile the zonal organization of the market with a pricing system that supports efficient real-time dispatch. In this paper, we study the problem of capacity expansion under zonal pricing with market-based re-dispatch. We propose a formulation of the problem as a mixed linear complementarity problem and analyze the existence and efficiency of solutions, both from a theoretical and empirical perspective. We find that zonal pricing with market-based re-dispatch leads to large efficiency losses. Moreover, although there exist theoretical conditions under which the efficiency of the design could be improved by means of regulatory interventions, the strictness of these conditions renders their practical implementation difficult and, therefore, the full recovery of the efficiency unlikely.
2022
-
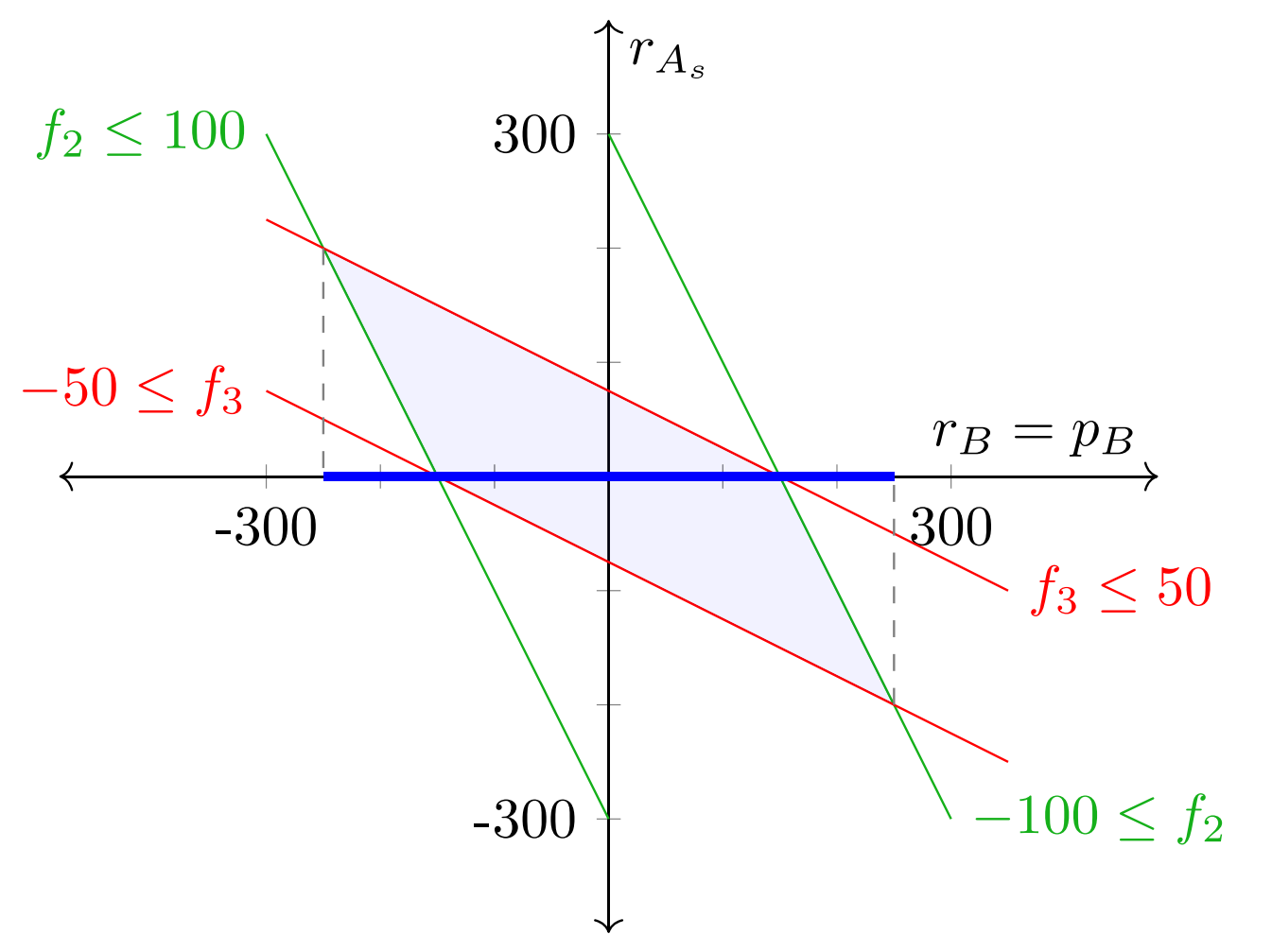 An analysis of zonal electricity pricing from a long-term perspectiveQuentin Lété, Yves Smeers, and Anthony PapavasiliouEnergy Economics, 2022
An analysis of zonal electricity pricing from a long-term perspectiveQuentin Lété, Yves Smeers, and Anthony PapavasiliouEnergy Economics, 2022In an era of energy transition, it is crucial to ensure that the design of the short-term electricity market provides sufficient cash flows to producers so as to allow the investment of the right technology at the right location. In this paper, we revisit the question of capacity allocation in zonal markets from a long-term perspective. We model the capacity expansion problem in zonal markets in which inter-zonal transmission capacity allocation is organized through flow-based market coupling, which is an approximation of power flow equations in aggregate networks that is employed in European market design. We demonstrate that the classical result of equivalence between centralized and decentralized formulations in transmission-constrained markets ceases to hold in this case. We propose a model of the decentralized capacity expansion problem with flow-based market coupling as a generalized Nash equilibrium that we formulate as a linear complementarity problem. We then perform simulations of the capacity expansion problem with nodal pricing and three variations of zonal pricing on a realistic instance of the Central Western European network and comment on the impacts of flow-based market coupling on investment.
2021
-
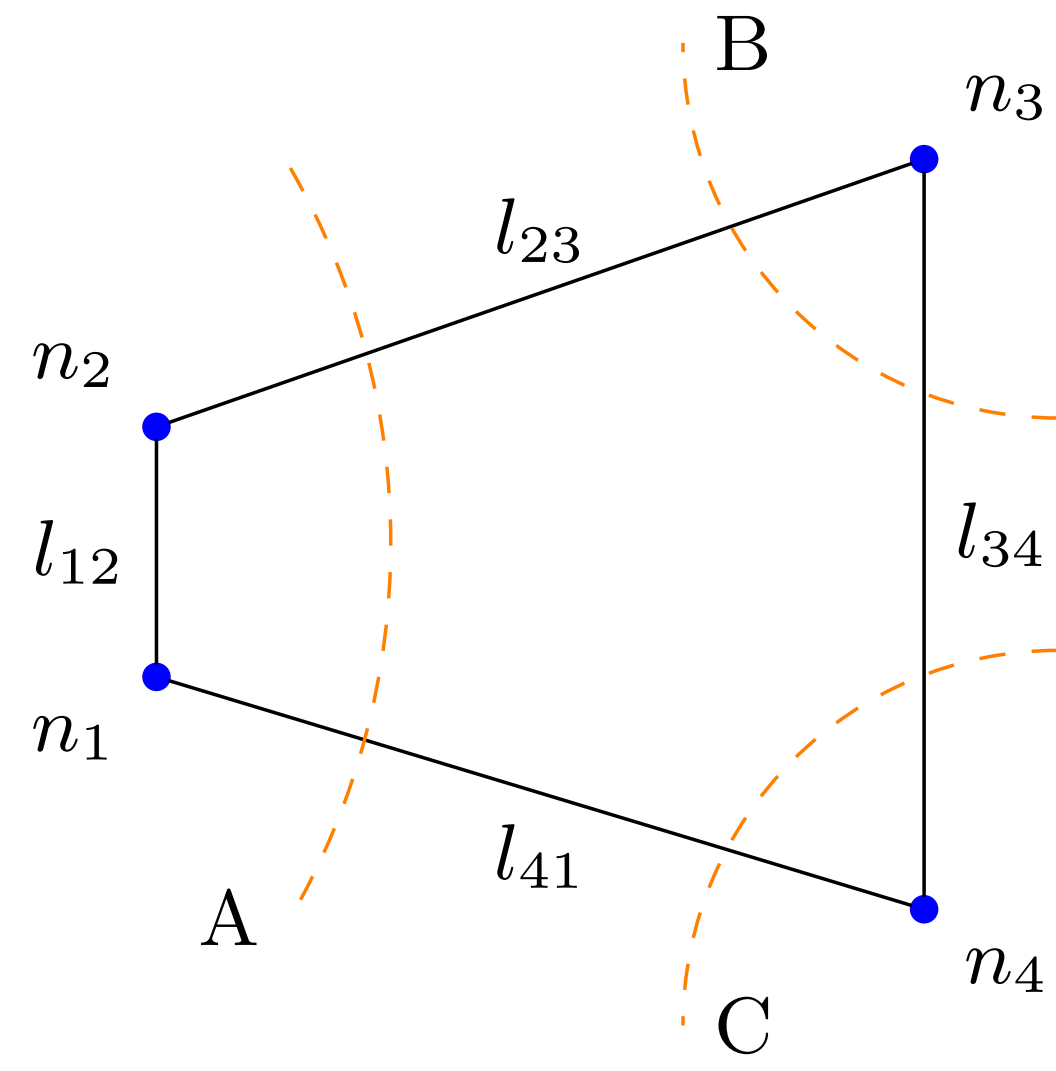 Transmission Capacity Allocation in Zonal Electricity MarketsIgnacio Aravena, Quentin Lété, Anthony Papavasiliou , and 1 more authorOperations Research, 2021
Transmission Capacity Allocation in Zonal Electricity MarketsIgnacio Aravena, Quentin Lété, Anthony Papavasiliou , and 1 more authorOperations Research, 2021We propose a novel framework for modeling zonal electricity markets, based on projecting the constraints of the nodal network onto the space of the zonal aggregation of the network. The framework avoids circular definitions and discretionary parameters, which are recurrent in the implementation and study of zonal markets. Using this framework, we model and analyze two zonal market designs currently present in Europe: flow-based market coupling (FBMC) and available-transfer-capacity market coupling (ATCMC). We develop cutting-plane algorithms for simulating FBMC and ATCMC while accounting for \anthonythe robustness of imports/exports to single element failures, and we conduct numerical simulations of FBMC and ATCMC \anthonyon a realistic instance of the Central Western European system under the equivalent of 100 years of operating conditions. We find that FBMC and ATCMC are unable to anticipate \anthonythe congestion of branches interconnecting zones and branches within zones, and that both zonal designs achieve similar overall cost efficiencies (0.01% difference), while a nodal market design largely outperforms both of them (5.09% better than FBMC). These findings raise the question of whether it is worth for more European countries to switch from ATCMC to FBMC, instead of advancing directly towards a nodal market design.
-
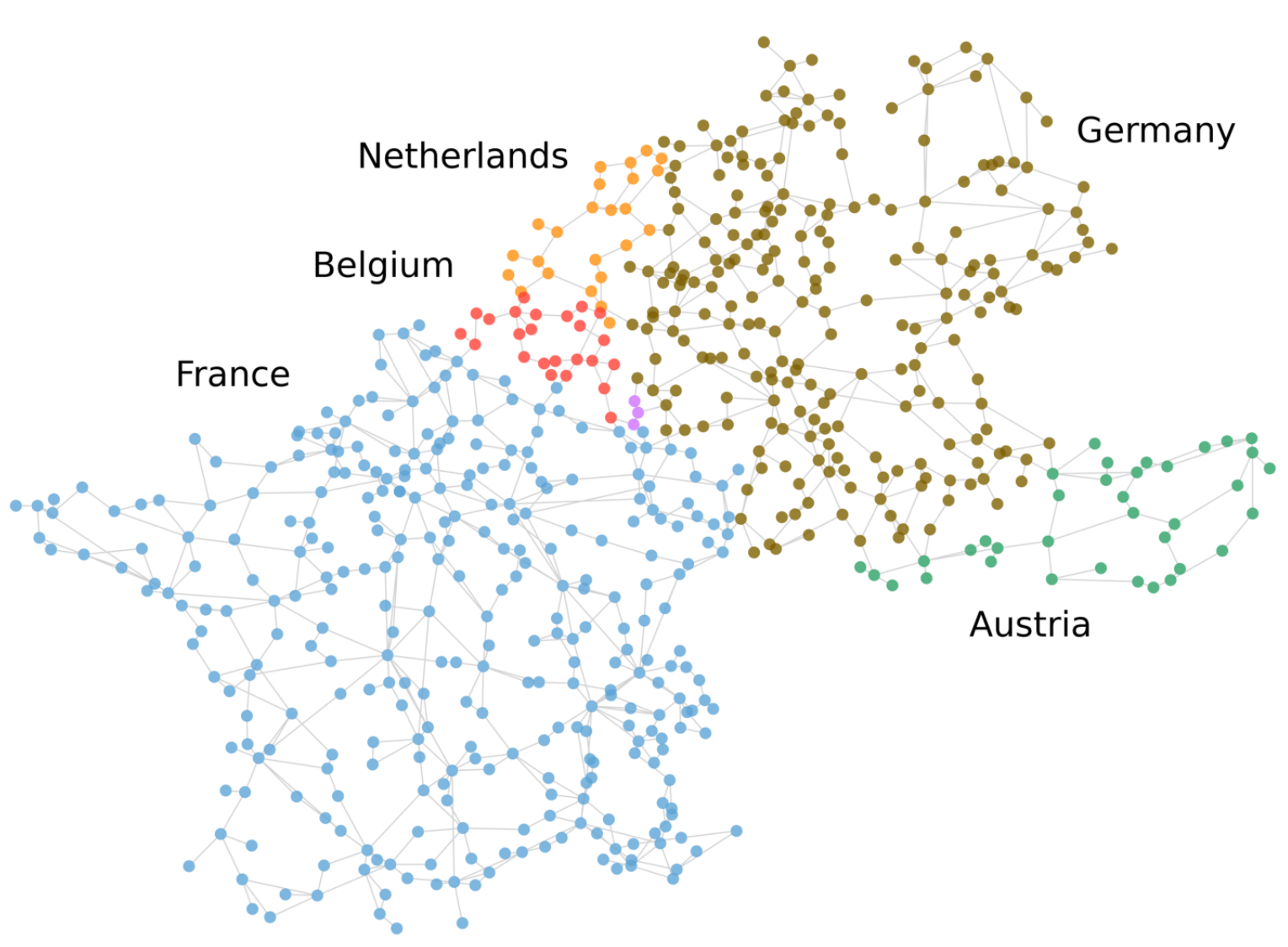 Impacts of Transmission Switching in Zonal Electricity Markets - Part IQuentin Lété, and Anthony PapavasiliouIEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021
Impacts of Transmission Switching in Zonal Electricity Markets - Part IQuentin Lété, and Anthony PapavasiliouIEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021In this paper, we present a two-stage model of zonal electricity markets with day-ahead market clearing and real-time re-dispatch and balancing that accounts for transmission line switching at both stages. We show how the day-ahead problem with switching can be formulated as an adaptive robust optimization problem with mixed integer recourse and present a new algorithm for solving the adversarial max-min problem that obeys the structure of an interdiction game. We apply the model on a realistic instance of the Central Western European system and comment on the impacts of both proactive and reactive transmission switching on the operating costs of the system. Part I presents day-ahead models of a short-term zonal electricity market with switching, and describes our algorithmic approach for solving these models efficiently. Part II describes variants of the real-time model, and presents the results of our case study on the Central Western European market.
-
 Impacts of Transmission Switching in Zonal Electricity Markets - Part IIQuentin Lété, and Anthony PapavasiliouIEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021
Impacts of Transmission Switching in Zonal Electricity Markets - Part IIQuentin Lété, and Anthony PapavasiliouIEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2021In this paper, we present a two-stage model of zonal electricity markets with day-ahead market clearing and real-time re-dispatch and balancing that accounts for transmission line switching at both stages. We show how the day-ahead problem with switching can be formulated as an adaptive robust optimization problem with mixed integer recourse and present a new algorithm for solving the adversarial max-min problem that obeys the structure of an interdiction game. We apply the model on a realistic instance of the Central Western European system and comment on the impacts of both proactive and reactive transmission switching on the operating costs of the system. Part I presents day-ahead models of a short-term zonal electricity market with switching, and describes our algorithmic approach for solving these models efficiently. Part II describes variants of the real-time model, and presents the results of our case study on the Central Western European market.